Nội dung và yêu cầu cần giải quyết trong nhiệm vụ làm luận văn tốt nghiệp (lý thuyết, thực hành, số liệu cần tính toán và hình vẽ). Đánh giá chất lượng luận văn (so với yêu cầu nội dung đề ra trong bài tập của Đ.T.T.N về mặt lý luận, thực tiễn, tính toán giá trị sử dụng, chất lượng bản vẽ). Đánh giá chất lượng đồ án tốt nghiệp về thu thập và phân tích tài liệu, số liệu ban đầu, giá trị lý luận và thực tiễn của đồ án.
INTRODUCTION
- R ATIONALE
- A IMS OF THE S TUDY
- R ESEARCH Q UESTIONS
- S COPE OF THE S TUDY
- M ETHODS OF THE S TUDY
- S IGNIFICANCE OF THE S TUDY
- D ESIGN OF THE S TUDY
- THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
- Listening
- The Role of Note Taking Skill in Listening
- What to Note
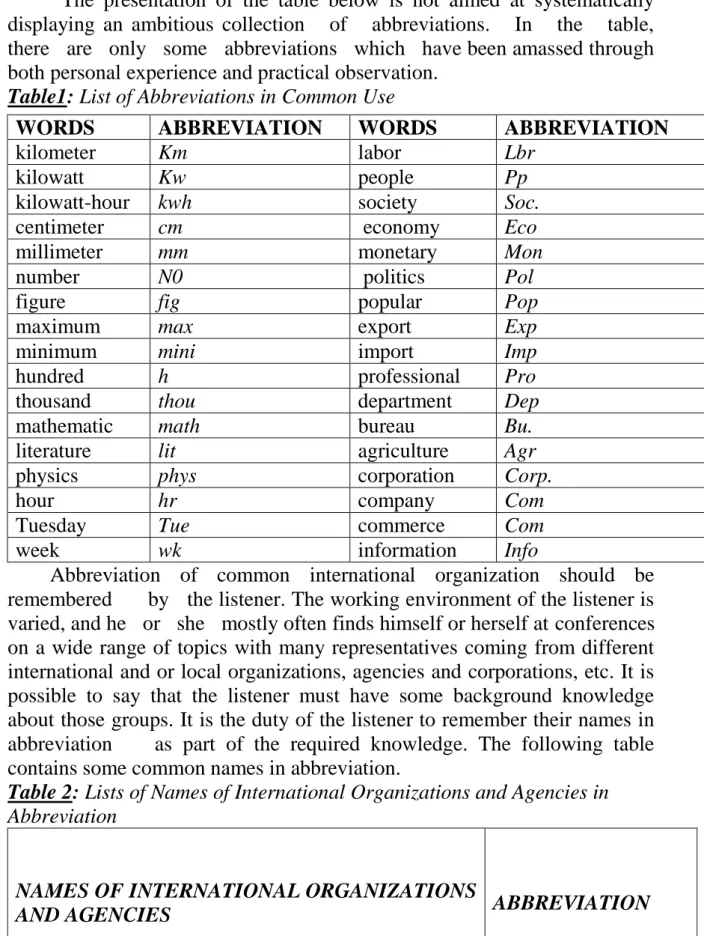
The important aspect of this type of listening is whether the listener understands the message conveyed by the speaker. The second thing the listener should keep in mind when taking notes is the connections between ideas. Therefore, it is no exaggeration to say that numbers, proper names, lists, and terminologies are the most deserving of priority in listener note-taking.
In summary, the listener's notes should at least show the main ideas and the connections between them to help the listener visualize the structure of the speech. It is not recommended to distract the listener from his work for any reason. Abbreviations help the listener take notes quickly, saving time spent on other activities in the listening process.
These abbreviations must be unambiguous and unambiguous enough that the listener can immediately understand when. It is the duty of the listener to remember their names in abbreviations as part of the required knowledge. Any symbol improvised in the middle of listening can drive the listener into a difficult and intense situation.
A basic rule for the listener: use only those symbols that are already fixed in the mind. This means that symbols are immediately associated for the listener himself with the meaning he gives them. By paying attention to this point, the listener can avoid mistakenly "deciphering" the meaning of the symbols he or she uses.
What good are abbreviations and symbols if they don't help the listener to do their job better. Depending on the structure, the listener can add other details to the notes if they wish. There are different opinions about which language the listener should use in the notes: source or target language.
Moreover, when taking notes in the target language, the listener cannot have “a complete set of notes at the end of a speech.” While taking notes, the listener is constantly tasked with making decisions.
METHODS AND PROCEDURES
- I NTRODUCTION
- T HE O BJECTIVE OF THE S URVEY
- S UBJECTS
- M ETHODOLOGY AND M ETHOD OF THE S URVEY
- Methodology
- Method
- P ROCEDURES
- DATA ANALYSIS
- A NALYZING FROM THE STUDENTS ’ SURVEY QUESTIONNAIRE
- A NALYZING F ROM THE T EACHERS ’ S URVEY Q UESTIONNAIRE
In fact, 50 copies of the survey were distributed and the number returned was 45. At the end of the first hour of the in-depth sequential listening test, approximately 50 students were asked to complete the survey. It is a reorganization of students' common problems in studying listening skills with questionnaire data using pie charts and columns that correspond to the sequence of questions and immediately draw conclusions on each picture.
The above diagram illustrates the role of listening from the students' point of view. 100% of students admitted that listening is very important to them. As the chart shows, up to 90% of students sometimes or rarely practice the skill of note-taking at home, and only 10% of them do it as a habit every day. Students' time allocation for self-study at home is also a problem and has a major impact on students in mastering the skill of note-taking.
As the graph shows, almost half of the teaching staff at the Faculty of Foreign Languages think that their students' listening skills are at an average level during the first two years. It can be concluded that the biggest challenge for students in the early years is note taking. Therefore, varying accents become one of the problems that English majors face in listening comprehension.
54% of teachers admitted that they feel stress and intonation due to students' obstacles in understanding the message. Another phonological factor that affects students' listening ability is connected speech, according to teachers. In addition, the majority of lecturers (64%) believe that the ability to take notes is not good enough to take good notes.
These factors together with hearing problems do not seem to be the major challenges for students when only 9% of teachers complain of hearing problems. As can be seen from the pie chart, 45% of teachers believe that the materials currently used for Year 2 English majors are interesting and appropriate. Unlike 40% of students, all teachers believe that the textbooks for teaching note taking are appropriate and interesting for the students' skill level.
CONCLUSION
C ONCLUSION
If the listener tries to write down words, not ideas, he or she always would.
S OME SUGGESTED TECHNIQUES
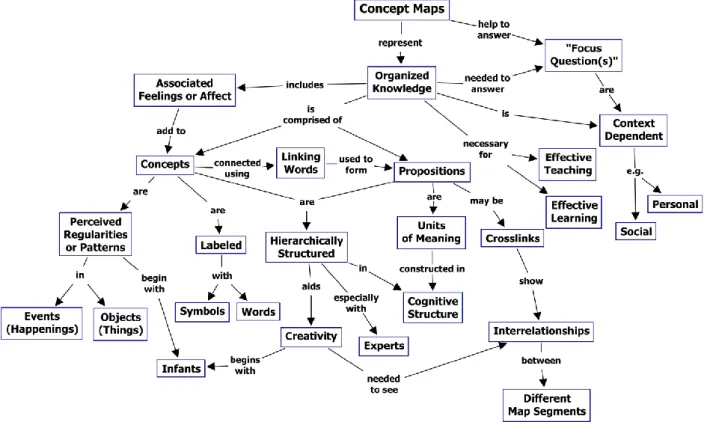
- U SE S YMBOLS AND A BBREVIATIONS
- U SE C ONCEPT M APS AND D IAGRAMS
- T AKING N OTES IN C LASS : A B RIEF S UMMARY
- Before the Lecture Begins
- During the Lecture
- After the Lecture
- OTHER SUGGESTED TECHNIQUES ON TAKING NOTES
- The 2-6
- Split Page Method
- Using Group Notes
- Secrets to Taking Better Notes
- Noteworthy Notes
- Attend Class
- Prepare for the lecture
- Use Colors
Grasping the idea and then writing it down is one of the basics of note-taking. So just write some key words, numbers and information that contribute to the recall of the information flow. Once a topic or question is decided, it will help with the hierarchical structure of the concept map.
Using highlighters, underlining, capitalizing or asterisks will help key ideas stand out from other notes. You'll find that effective note-taking is a skill that's extremely important in college, but it's also a skill that will be valuable in your professional life. As with terms and definitions, memorize the parts of the text or reading assignment that you do not understand.
Make sure you have all the materials you need for class, such as a pen and paper. Doing so can greatly speed up your note-taking and thus increase the number of notes you can take during class. Try to develop a general picture of the material underlying the course instead of simply memorizing facts and equations.
Make two columns, using the red line on the left side of the page as a border. Take class notes on one side of the page and outline the text on the other side. In addition to attending class, it's important to improve your note-taking skills to truly achieve optimal success.
If you have something written down on paper, you can always refer to the material later. Writing in color will help you retain 50% - 80% more information without reading it a second time (also highlight in purple). According to these things, students will better improve their note-taking skills in listening class.
Suggestions for Further Study
This questionnaire is designed for the investigation of some obstacles faced by HPU 2nd year English majors in listening comprehension. All the information provided is solely for the purpose of the survey, not for any other purpose. Among four skills: reading, speaking, writing and listening, listening skills are the most difficult for you.
Do you think that listening material applicable to the 2nd year English majors is interesting and appropriate. In your opinion, what should your teachers do to help you improve your listening skills. This questionnaire is designed for the study on techniques to improve note-taking skills in listening class for HPU 2nd year English major.
All information provided is for study purposes only and not for any other purpose. How do you assess your students' listening skills during their first two years of college? Do you think listening material for 2nd year English majors is interesting and appropriate?